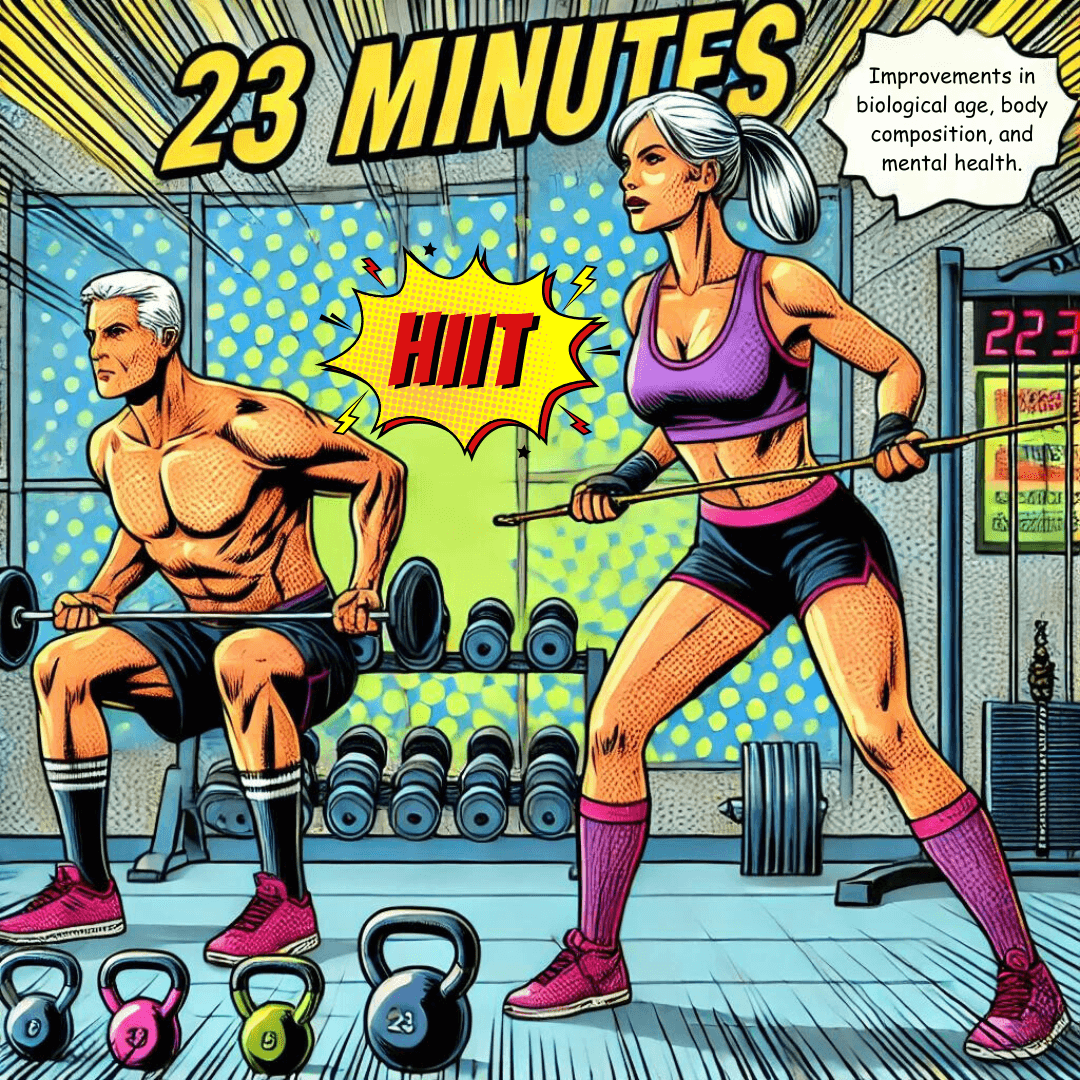
Exercise is widely known to help increase life span, but its specific effects on biological age are less clear.
A recent study used a transcriptomic age (TA) predictor to examine how high-intensity interval training (HIIT) affects biological age (Lohman T, et.al., 2023).
The study involved 30 sedentary adults aged 40-65, divided into a HIIT group and a no-exercise control group.
The HIIT group did three 23-minute sessions per week for four weeks. Results showed that HIIT reduced biological age by 3.59 years, while the control group's biological age increased by 3.29 years.
Additionally, the HIIT group saw improvements in body composition and mental health measures.
This suggests that even a small amount of HIIT can significantly impact biological age and health in sedentary middle-aged adults.
Learn how to exercise for maximum benefits while spending minimum time with our exercise program.
Reference: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37078430/
Lohman T, Bains G, Cole S, Gharibvand L, Berk L, Lohman E. High-Intensity interval training reduces transcriptomic age: A randomized controlled trial. Aging Cell. 2023 Jun;22(6):e13841.