Description
This is not a regular B vitamin formula. The B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B6 (pyridoxine), and B12 (methylcobalamin) come in their physiologically active form, making them easier to absorb. As an example only 33% of the patients responded with an increased level of blood pyridoxal-5’-phosphate when receiving pyridoxine HCL the most common form of B6, but the level increased in all when given the pyridoxal-5’-phosphate (Labadarios D, et al. 1977).
Blood levels have shown to be higher from using 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, the metabolite of folic acid as compared to using folic acid (Willems FF, et al. 2004).
Research has shown that benfotiamine a form of vitamin B1 raised blood and tissue levels higher and also remained bioavailable much longer after taking it orally when compared to the more common form of B1 (Loew D, et al. 1996). Benefotiamine has shown to decrease the glucose metabolites that lead to the buildup of certain types of detrimental advanced glycation end products, it protects the retina and it may also protect the kidneys and endothelial cells (Thornalley PJ, 2005, Stirban A, et al. 2006).
B-vitamins are important for many reasons and especially the nervous systems but also for the cardiovascular system. A deficiency of Vitamin B6, B12 and folic acid have been linked to elevated levels of the amino acid homocysteine. Increased homocysteine is recognized as a risk factor for several serious conditions.
• In a study using MRI markers of neuropathy (abnormality), the researchers concluded that elevated homocysteine and low folate were associated with radiological markers of neuropathology (Scott TM, et al. 2004).
• Low folic acid and high homocysteine levels are correlated with depressive symptoms in middle aged individuals (Sachdev PS, et al. 2005, Tolmunen T, et al. 2004).
• Elevated plasma homocysteine and low serum folate are independent predictors of the development of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease (Ravaglia G, et al. 2005, Quadri P, et al. 2004).
• Low levels of vitamin B6, B12, folic acid and elevated levels of homocysteine predicted cognitive decline (loss of memory) (Tucker KL, et al. 2005).
• Deficiency of vitamin B12 has been associated with elevated levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha an inflammatory marker (Scalabrino G, et al. 2004, Peracchi M, et al. 2001, Miller JW. 2002).
• High plasma homocysteine concentrations and low concentrations of folic acid and vitamin B6 are associated with an increased risk of extracranial carotid artery stenosis (Selhub J, et al. 1995).
The carotid arteries are blood vessels going up to the brain. Stenosis of an artery means the artery is obstructed to a more or less degree depending on the severity of the stenosis.
• Higher folate intake lowers the risk for peripheral artery disease when compared to lower intake (Merchant AT, et al. 2003).
• Folic acid supplementation has shown to lower plasma homocysteine levels and improve insulin and lipid metabolism in healthy postmenopausal women, reducing the risk for cardiovascular disease (Villa P, et al. 2005).
• Homocysteine and vitamin B12 has shown to be associated with bone mineral density (Morris MS, et al. 2005).
• Increased levels of homocysteine has been associated with increased breast cancer risk in women who have below median levels of folic acid (Goodman JE, et al. 2001).
• A hypothesis predicts that adequate intake of folic acid, vitamin B6 and B12 may reduce hyperhomocystemia associated risk for hormonal cancer (Zhu BT. 2003).
Vitamin B-complex from BioPro, Inc. also includes the metabolite of folic acid, since not everybody metabolizes folic acid properly.
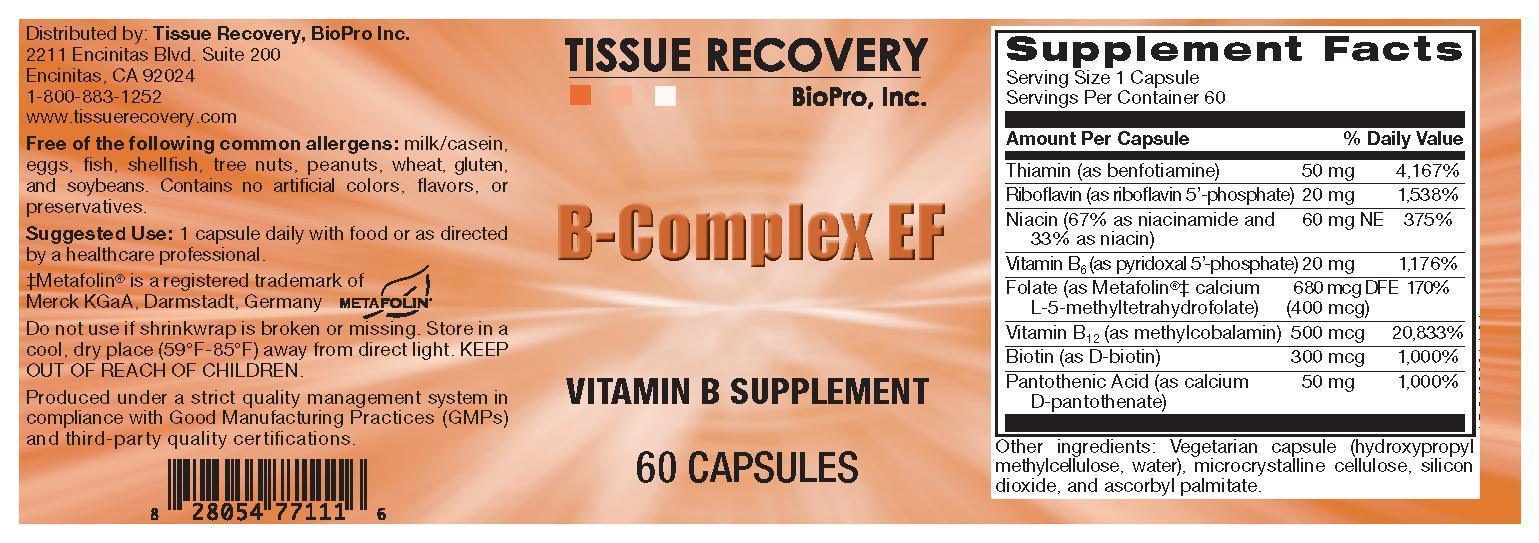
|
Serving Size 1 Capsule |
||
|
Amount Per Capsule |
% Daily Value |
|
|
Thiamin (as benfotiamine) |
50 mg |
4,167% |
|
Riboflavin (as riboflavin 5’-phosphate) |
20 mg |
1,538% |
|
Niacin (67% as niacinamide and 33% as niacin) |
60 mg NE |
375% |
|
Vitamin B6 (as pyridoxal 5’-phosphate) |
20 mg |
1,176% |
|
Folate (as Metafolin®‡ calcium L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate) |
680 mcg DFE |
170% |
|
Vitamin B12 (as methylcobalamin) |
500 mcg |
20,833% |
|
Biotin (as D-biotin) |
300 mcg |
1,000% |
|
Pantothenic Acid (as calcium D-pantothenate) |
50 mg |
1,000% |
Other Ingredients:
Vegetarian capsule (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, water), microcrystalline cellulose, silicon dioxide, and ascorbyl palmitate.
‡Metafolin® is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany.
References:
Goodman JE, Lavigne JA, Wu K, Helzlsouer KJ, Strickland PT, Selhub J, Yager JD. COMT genotype, micronutrients in the folate metabolic pathway and breast cancer risk. Carcinogenesis. 2001 Oct;22(10):1661-5.
Labadarios D, Rossouw JE, McConnell JB, Davis M, Williams R. Vitamin B6 deficiency in chronic liver disease–evidence for increased degradation of pyridoxal-5′-phosphate. Gut. 1977 Jan;18(1):23-7.
Loew D. Pharmacokinetics of thiamine derivatives especially of benfotiamine. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1996 Feb;34(2):47-50.
Merchant AT, Hu FB, Spiegelman D, Willett WC, Ascherio A. The use of B vitamin supplements and peripheral arterial disease risk in men are inversely related. J Nutr. 2003 Sep;133(9):2863-7.
Miller JW. Homocysteine, folate deficiency, and Parkinson’s disease. Nutr Rev. 2002 Dec;60(12):410-3.
Morris MS, Jaques PF, Selhub J. Relation between homocysteine and B-vitamin status indicators and bone mineral density in older Americans. Bone. 2005 Aug;37(2):234-42.
Peracchi M, Bamonti Catena F, Pomatl M, et al. Human cobalamin deficiency: alterations in serum tumour necrosis factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor. Eur J Haematol. 2001 Aug;67(2):123-7.
Quadri P, Fragiacomo C, Pezzati R, Zanda E, Fortoni G, Tettamanti M, Lucca U. Homocysteine, folate, and vitamin B-12 in mild cognitive impairment Alzheimer disease, and vascular dementia. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004 Jul; 80(1):114-22.
Ravaglia G, Forti P, Maioli F, Martelli M, et al. Homocysteine and folate as risk factors for dementia and Alzheimer diease. Am J Nutr. 2005 Sep;82(3):636-43.
Sachdev PS, Parslow RA, Lux O, et al. Relationship of homocysteine, folic acid and vitamin B12 with depression in a middle-aged community sample. Psychol Med. 2005 Apr;35(4):529-38
Scalabrino G, Carpo M, Bamonti F, Pizzinelli S, et al. High tumor necrosis factor-alpha [corrected] levels in cerebrospinal fluid of cobalamin-deficient patients. Ann Neurol. 2004 Dec;56(6):886-90
Scott TM, Tucker KL, Bhadelia A, Benjamin B, Patz S, et al. Homocysteine and B vitamins relate to brain volume and white-matter changes in geriatric patients with psychiatric disorders. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2004 Nov-Dec; 12(6):631-8.
Selhub J, Jacques PF, Bostom AG, D’Agostino RB, Wilson PW, et al. Association between plasma homocysteine concentrations and extracranial carotid-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med. 1995 Feb 2;332(5):286-91.
Stirban A, Negrean M, Stratmann B, Gawlowski T, Horstmann T, Götting C, Kleesiek K, Mueller-Roesel M, Koschinsky T, Uribarri J, Vlassara H, Tschoepe D. Benfotiamine prevents macro- and microvascular endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress following a meal rich in advanced glycation end products in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006 Sep;29(9):2064-71.
Thornalley PJ. The potential role of thiamine (vitamin B1) in diabetic complications. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2005 Aug;1(3):287-98.
Tolmunen T, Hintikka J, Voutilainen S, Ruusunen A, et al. Association between depressive symptoms and serum concentrations of homocysteine in men: a population study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004 Dec;80(6):1574-8.
Tucker KL, Qiao N, Scott T, Rosenberg I, Spiro A 3rd. High homocysteine and low B vitamins predict cognitive decline in aging men: the Veterans Affairs Normative Aging Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005 Sep;82(3):627-35.
Villa P, Perri C, Suriano R, Cucineeli F, Panunzi S, et al. L-folic acid supplementation in healthy postmenopausal women: effect on homocysteine and glycolipid metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Aug;90(8):4622-9.
Willems FF, Boers GH, Blom HJ, Aengevaeren WR, Verheugt FW. Pharmacokinetic study on the utilisation of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and folic acid in patients with coronary artery disease. Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Mar;141(5):825-30. Epub 2004 Feb 9.
Zhu BT. Medical hypothesis: hyperhomocysteinemia is a risk factor for estrogen-induced hormonal cancer. Int J Oncol. 2003 Mar;22(3):499-508.








There are no reviews yet.