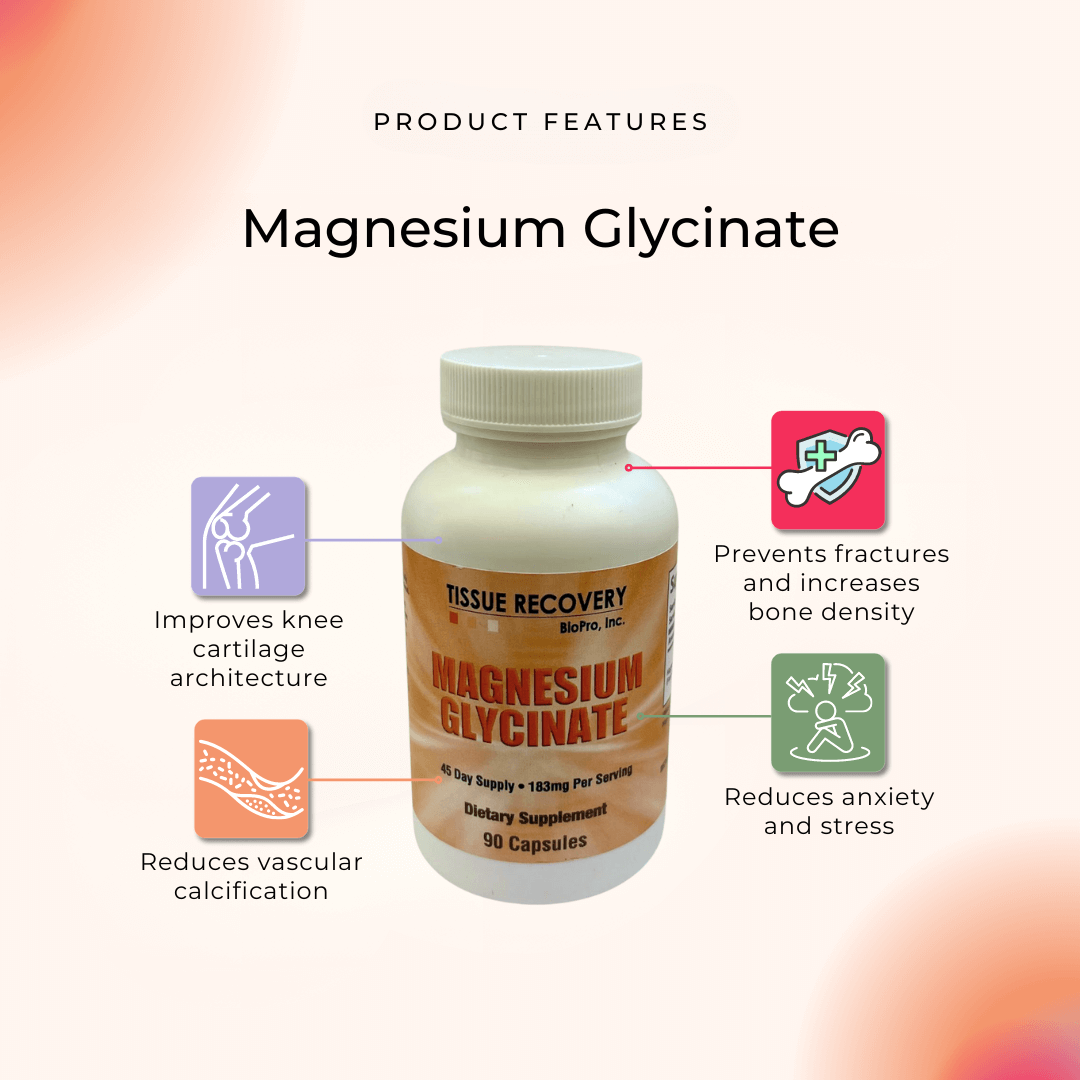
Increased magnesium intake is associated with better knee cartilage architecture (Veronese N, et.al., 2019).
Magnesium has shown to prevent fractures and increase bone density (Sojka JE, Weaver CM. 1995, Stendig-Lindberg G, et al. 1993).
Research has documented that increasing magnesium levels significantly reduced vascular calcification (Louvet L, et al. 2013, Hruby A, et al. 2014).
Anxiety and stress have been associated with magnesium deficiencies (Grases G, et.al., 2006, Cernak I, et.al., 2000).
References:
Cernak I, Savic V, Kotur J, Prokic V, Kuljic B, Grbovic D, Veljovic M. Alterations in magnesium and oxidative status during chronic emotional stress. Magnes Res. 2000 Mar;13(1):29-36.
Grases G, Pérez-Castelló JA, Sanchis P, Casero A, Perelló J, Isern B, Rigo E, Grases F. Anxiety and stress among science students. Study of calcium and magnesium alterations. Magnes Res. 2006 Jun;19(2):102-6.
Hruby A, O'Donnell CJ, Jacques PF, Meigs JB, Hoffmann U, McKeown NM. Magnesium intake is inversely associated with coronary artery calcification: the Framingham Heart Study. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014 Jan;7(1):59-69.
Louvet L, Büchel J, Steppan S, Passlick-Deetjen J, Massy ZA. Magnesium prevents phosphate-induced calcification in human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Apr;28(4):869-78.
Veronese N, La Tegola L, Caruso MG, Maggi S, Guglielmi G. The Association between Dietary Magnesium Intake and Magnetic Resonance Parameters for Knee Osteoarthritis. Nutrients. 2019 Jun 20;11(6):1387.
Sojka JE, Weaver CM. Magnesium supplementation and osteoporosis. Nutr Rev. 1995 Mar;53(3):71-4.
Stendig-Lindberg G, Tepper R, Leichter I. Trabecular bone density in a two year controlled trial of peroral magnesium in osteoporosis. Magnes Res. 1993 Jun;6(2):155-63.